German Fiscal Stimulus
Germany is poised to implement a significant fiscal stimulus package aimed at revitalizing its economy and addressing long-standing infrastructure deficits. The German economy has been struggling in recent years and faces continued challenges in 2025:
Germany experienced a GDP contraction of 0.3% in 2023 and 0.2% in 2024.
The economy has been largely stagnant since Q4 2019, with real GDP unchanged over that period.
The German government recently slashed its 2025 GDP growth forecast from 1.1% to just 0.3%.
Goldman Sachs Research forecasts 0.3% growth for Germany in 2025, lagging behind projections of 0.8% for the eurozone and 1.2% for the UK.
The Roland Berger Institute projects a modest 0.4% GDP growth for 2025, placing Germany behind other G20 nations.
The unemployment rate rose to 6.2% in February 2025, the highest level since October 2020.
Only one in eight German companies anticipates "somewhat favorable" prospects for 2025. One in three companies expects "somewhat unfavorable" developments, with concerns particularly pronounced in the retail and construction sectors.
Key Challenges
High energy costs and administrative burdens.
Growing global protectionist tendencies, especially uncertainty in trade relations with the US.
Increasing competition from China.
Political uncertainty following the collapse of the coalition government in late 2024
STIMULUS PACKAGE
The key elements of this stimulus plan include:
€500 Billion Infrastructure Fund
A special off-budget infrastructure fund totaling €500 billion over the next decade has been proposed.
This fund aims to invest in various sectors, including transportation, energy, education, and digitalization.
The construction industry is expected to be a major beneficiary, with companies like Heidelberg Materials, Bilfinger, and Hochtief seeing significant stock price increases.
Debt Brake Reform
The coalition parties have agreed to amend Germany's constitutionally enshrined "debt brake".
The proposed changes would exempt defense spending exceeding 1% of GDP from borrowing constraints.
This reform aims to provide greater fiscal flexibility to address current economic challenges.
Additional Measures
A "growth package" of 49 concrete measures, including bureaucracy reduction and incentives for workers, has been proposed.
Plans for a "Deutschlandfonds" to encourage investments, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises, large corporations, and startups.
A proposed "non-bureaucratic" investment premium of 10% for all companies.
Economic Impact
Economists predict that swift implementation of these measures could lead to a significant uptick in growth, potentially reaching rates of 2% in the coming years.
The stimulus is expected to boost various sectors, including construction, defense, and energy.
German defense firms like Rheinmetall, Hensoldt, and Renk have already seen substantial increases in their stock prices due to the proposed changes.
This fiscal stimulus represents a major shift in German economic policy, moving away from the traditionally conservative approach to a more expansive stance aimed at addressing structural weaknesses and boosting economic growth
Key Impacts on Bond Yields
Rising German Bund Yields:
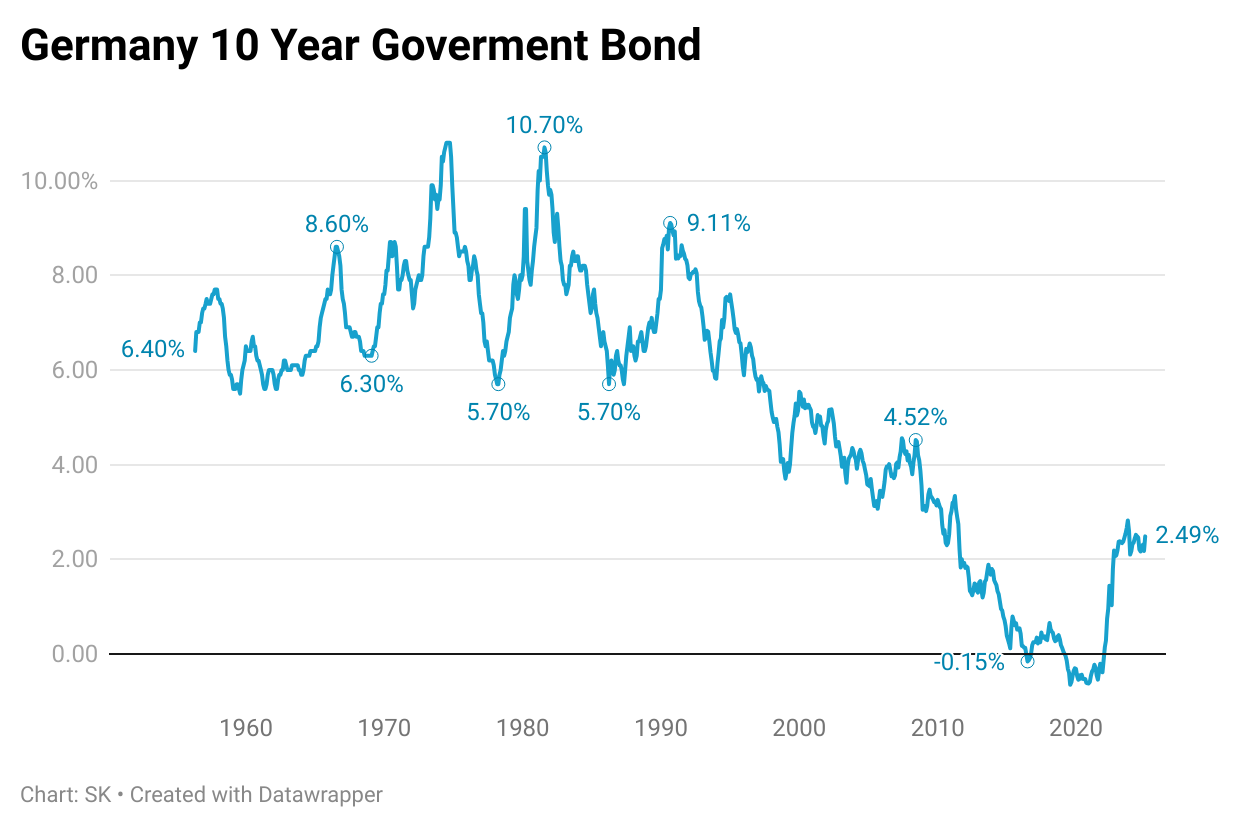
The yield on Germany's 10-year Bunds surged to 2.86%, marking its largest weekly increase since the 1990s, with a 30-basis-point jump in a single day following the announcement. This is the highest level seen in nearly three years.
Goldman Sachs projects that 10-year Bund yields could climb further, potentially reaching 3.75%, levels not seen since 2008.
Global Bond Market Ripple Effects:
German Bunds, considered a benchmark for eurozone debt, have influenced yields on other European government bonds. For example: